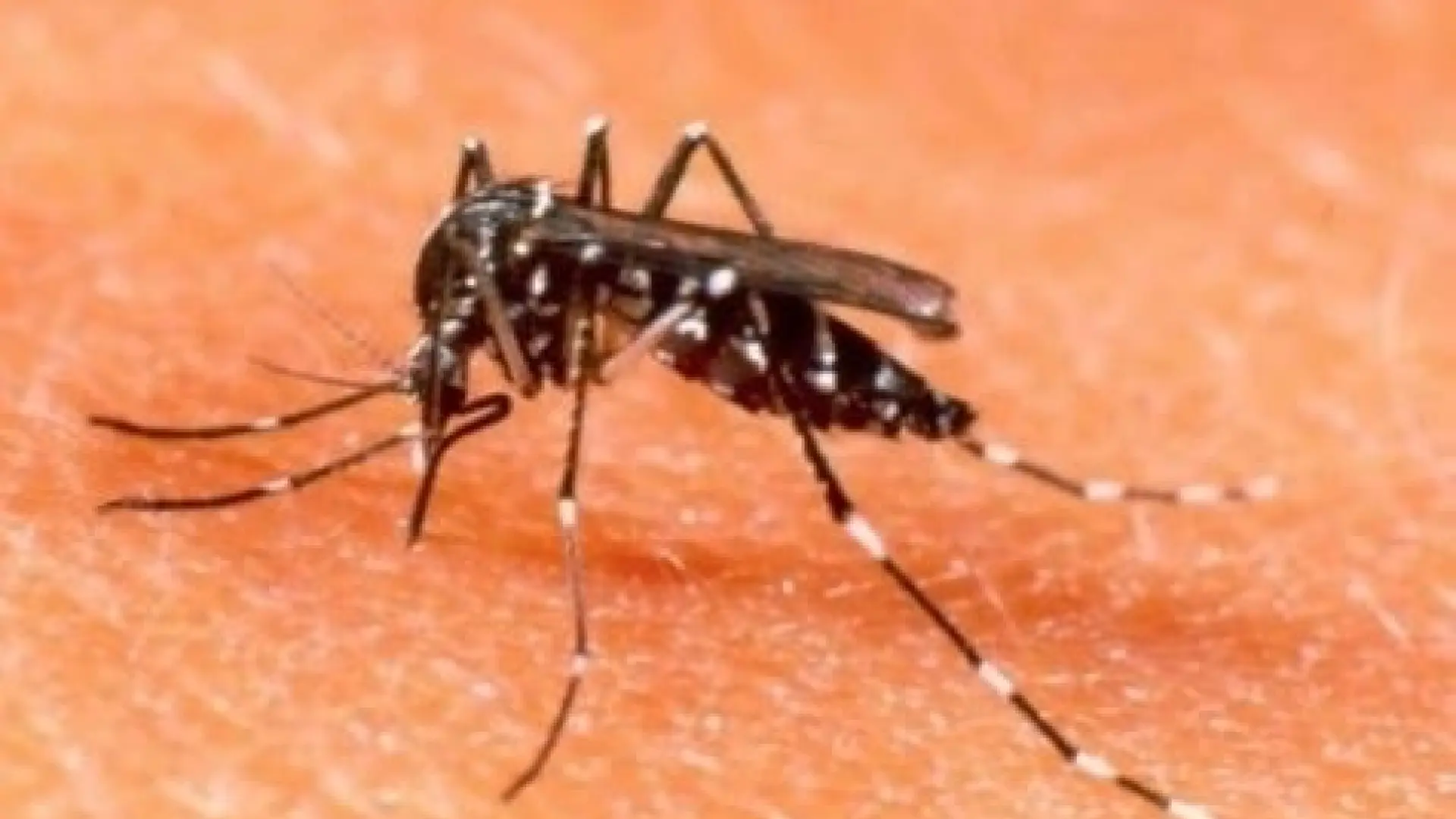
Hong Kong Center for Health Protection (CHP) investigating co-infection of 16-year-old male by viruses zika and dengue after returning to the previous British colony from Thailand on April 6.
One day after his arrival in Hong Kong, the younger man, who was beforehand in good well being, started to expertise fever, complications and eye discomfort.
After receiving hospital therapythe analyzes confirmed the presence of the Zika and dengue viruses in their blood samples.
Hong Kong well being authorities have taken measures to include and management the unfold of any virus in town and are additionally attempting to find out how coinfection occurred in the adolescentthe CHP reported final night time in an announcement.
These are illnesses of the arbovirus group, transmitted by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which have elevated each in incidence and geographical distribution, in a “advanced” epidemiological state of affairs as a result of variability of environmental situations and demographic and socioeconomic points, in response to the middle.

Both pathologies can produce a really related medical image, primarily throughout its acute section, thus making medical analysis by well being personnel troublesome.
Although many circumstances of Zika infection are asymptomatic or have gentle signs resembling fever, pores and skin rashes and muscle ache, this illness has been related to critical problems, resembling Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults or congenital malformations in newborns whose moms have been contaminated throughout being pregnant.
On the opposite hand, the dengue virus is characterised by inflicting related signs, however in some circumstances it may possibly progress to a extra critical kind that’s prone to trigger inner bleeding, organ injury and, in excessive circumstances, dying.
Dengue has skilled a spectacular international enhance in incidence over the previous twenty years, turning into a serious public well being drawback: in response to a model-based estimate, 390 million infections happen yearly by the dengue virus, of which 96 million manifest clinically.